- Australia - Climate
- Australia - People
- Australia - Case Studies
- New Zealand
- Africa - Location
- Africa - Case studies
Chapter 1. Australia - Climate, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
1. What are the factors that affect climate of Australia?
Factors that affect climate of Australia are Location, Distance from the Oceans, winds and direction of mountain ranges.
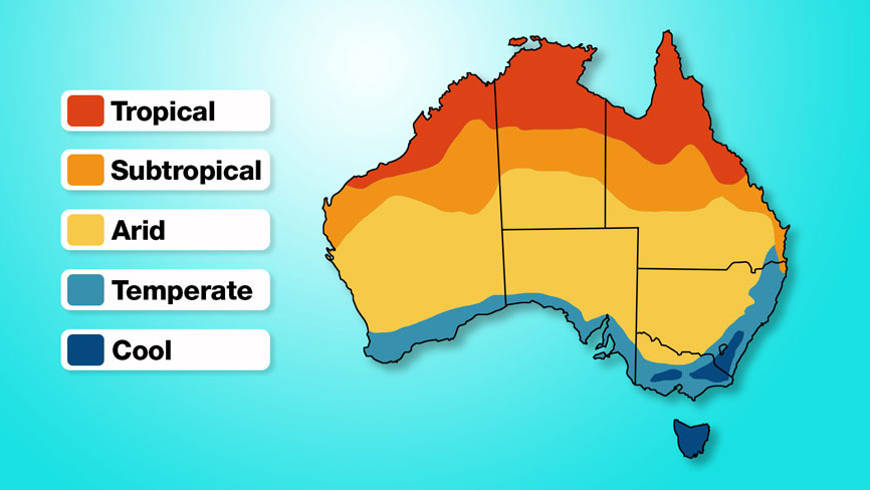
- Location: Australia is located in the Southern Hemisphere, and seasons are opposite of seasons in India. It is Summer in December and winter in July. Upper part of Australia which is above Tropic of Capricorn, lies in the tropical zone and has high temperature through out the year. Lower part of Australia, which is below Tropic of Capricorn, is in the temperate zone which has hot summer and cool winter.
- Distance from the Oceans: Australia is surrounded by seas all sides. Nearness of the ocean affects the climate. The coastal areas are cooler and wetter than the inland areas. Central parts of the continent experience extreme climate. They have high temperature in summer and low temperature in winter.
- Winds: Winds that blow from the sea often bring rain to the coast. They cause dry weather to the inland areas. Dry wind blowing in interior parts of continent and deserts have formed.
- Direction of Mountain Ranges: The Great Dividing Range runs parallel to the eastern coast. It acts as barrier to the winds blowing from south-east. Due to this, south-east has lot of rain. Due to this there is less rain in Western Plateau region. It is the rain shadow area of GDR.
1. List seasons and months
- Summer: December to February
- Autumn: March to May
- Winter: June to August
- Spring: September to November
2. Describe climate of Australia
| Zone | Climate type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Northern part | Tropical zone | High temperature through out the year. |
| Southern part | Temperate zone | Warm summer, cool winter. Greater difference in temperature. |
What are the different types of climate in Australia
- Tropical monsoon type climate
- Savanna type climate
- Desert type climate
- Mediterranean type climate
- Temperate type climate
- China type climate
1.3 Climatic Regions In Relation With Natural Vegetation And Wild Life
Climate and description
| Climate | Where? | Summer | Winter | Vegetation | Wildlife |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tropical monsoon | Northern most part of northern territory. Cape York region of Queensland | Hot and heavy rainfall | Cold and dry | Bamboo, palm, eucalyptus, cedar, birch | Marsupials - Kangaroo, koala, possum, Tasmanian devil, Lyrebird. |
| Savanna | central northern territory and south west parts of Queensland | Hot and moderate rainfall | Cold and dry | known as Parkland vegetation. eucalyptus. | lizards, snakes, crocodiles. snakes, tiger, copperhead |
| Desert | Western plateau - great sandy desert and Great Victoria Deserts. | Hot and dry | Cold and dry; Summers are hottest. | bushes, thorny shrubs, spiniflex, acacia. | monotremes, placental types of mammals. duck-bill platypus, echidna, Australian Dingo. |
| Mediterranean | south-east and south-west coasts | Hot and dry | Cold and moderate rainfall | pine, beech, kauri, jarrah, mallee bushes. | Kookaburras, black swans, cassowarys, bower birds, spoonbills |
| Temperate | Eastern parts of New South wales, Victoria, Tasmania. Found in Murray-Darling basin | Moderate warm and wet | Cold and dry | Temperate grasslands are known as Downs. Consists of short grasses. Temperate forests consists of deciduous forests, pine, beech. | worm lizard, striped legless lizard. |
| China type | South-east coast of Queensland and New South Wales | Hot and heavy rain | Mild and dry | eucalyptus and coniferous trees. | fish, shell, coral reef. Dangerous sea wildlife Great White Pointer shark, the Box Jellyfish and Blue-Ringed Octopus |
1.4 The Great Barrier Reef
Q. Give four characteristic features of temperate grasslands.
Ans. Four characteristic features of temperate grasslands are:
- Known as "Downs" in Australia, much of the temperate grasslands lie in the Murray-Darling Basin.
- Summers are hot while the winters are cold.
- The region receives average rainfall.
- The temperate grasslands consist of short grass. Towards the west where the rainfall begins to decrease, the grasslands get replaced by scrub and bushes.
Q. What type of climate prevails in the Western Plateau? Give two characteristic features of this type of climate.
The tropical desert covers a major portion of the Western Plateau and hence this region has a tropical desert type of climate. Two main characteristics of this type of climate are:
Summers and extremely hot and winters extremely cold. There is also wide difference between the daily ranges of temperature. This region receives less than 25 cm of rainfall annually.
Q. In what ways do the following factors affect the climate of Australia?
- Latitude
- Direction of mountain ranges
Ans. Latitude: The Tropic of Capricorn passes through the nearly the centre of Australia and hence the country falls under the influence of the trade winds.
Direction of mountain ranges: When moisture bearing trade winds strike the Eastern Highlands (running along the eastern coast), it rains on the eastern coast which lies on the windward side of the Eastern Highlands while the leeward side hardly receives any rainfall.
Q. What is the most important river system of Australia? Name any four features of this river system.
The most important river system of Australia is the Murray- Darling Basin. Four features of this river system are: The Murray is the main river of Australia while Darling is its tributary. This river system lies to the east of the Central Lowlands. Since the river Murray originates in the Australian Alps, it is a snow fed river and thus has sufficient water. The river Darling does not have much water and becomes dry during droughts. During excessive rains, it tends to change its course.
Q. Write a short note on the availability of water in Australia.
Australia is an island continent with limited water resources. Rainfall in the region is uneven, unreliable and low. Only about one eighth of the total rainwater flows on the surface while the rest is evaporated as most parts of Australia are desert like. The Murray-Darling river basin is the largest river basin in Australia. More than half of the water of this basin is used for irrigation and power generation. Australia has large quantities of underground water resources. It gets much of the underground water from the artesian basin.
2. Australia- People, Resources and their utilization
Australia: Economic Features
Australia: Industry, Transportation and Population
3. Australia - Case studies
4. New Zealand - Location, Physical Features, Climate, Resources and their utilization, People
5. Africa - Location, Political and Physical Features
7. Africa - Case studies
Click on question to show/hide answers.